Issue when trying to bind nginx on CentOS 7.4 to other port than 80
Problem:
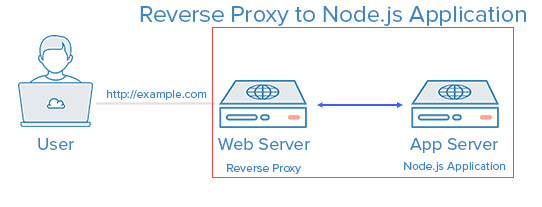
I was fighting with a permission related issue with nginx on CentOS 7.4. When I configure nginx to listen to port 80 everything works as expected, but when I use any other port (i.e. 82) it doesn’t.
[root@CentOS7 nginx]# sudo systemctl start nginx
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 systemd[1]: Starting The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server…
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 nginx[22626]: nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 nginx[22626]: nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:82 failed (13: Permission denied)
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 nginx[22626]: nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failed
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 systemd[1]: nginx.service: control process exited, code=exited status=1
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 systemd[1]: Failed to start The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server.
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 systemd[1]: Unit nginx.service entered failed state.
Mai 28 18:32:52 CentOS7 systemd[1]: nginx.service failed.
Solution:
This will most likely be related to SELinux
To check which ports are ports are allowed with SELinux and http use the following command
semanage port -l | grep http_port_t
http_port_t tcp 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
As you can see from the output above with SELinux in enforcing mode http is only allowed to bind to the listed ports.
The solution is to add the ports you want to bind on to the list
semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 82
will add port 82 to the list.
Now you can start nginx without any issues.
[root@CentOS7 nginx]# sudo systemctl start nginx [root@CentOS7 nginx]# sudo systemctl status nginx nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Do 2020-05-28 18:38:41 CEST; 6s ago Process: 22862 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 22859 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 22857 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 22864 (nginx) Tasks: 3 CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─22864 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx ├─22865 nginx: worker process └─22866 nginx: worker process Mai 28 18:38:41 CentOS7 systemd[1]: Starting The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server… Mai 28 18:38:41 CentOS7 nginx[22859]: nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok Mai 28 18:38:41 CentOS7 nginx[22859]: nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful Mai 28 18:38:41 CentOS7 systemd[1]: Started The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server.